2026 Best Roller Bearing Types for Enhanced Performance and Durability?
In the dynamic world of machinery, roller bearings play a pivotal role. They reduce friction and enhance efficiency. Experts are continually exploring new types for improved performance. John Smith, a renowned engineer in the roller bearing industry, states, "The right roller bearing can transform operational efficiency."
Different designs are emerging to meet specific demands. For instance, spherical roller bearings provide extra support under heavy loads. Their adaptability is crucial in various industries, from automotive to aerospace. However, selecting the right type is often overlooked. Improper choices can lead to premature wear and costly downtime.
The pursuit of the best roller bearing types is essential for success. With various materials and designs available, understanding their advantages is vital. Still, the market often lacks clear guidance. It's a challenge that beckons further exploration and learning. The right roller bearing can make a difference, but not all options are obvious.
Types of Roller Bearings: An Overview of Common Varieties
When considering roller bearings, it’s crucial to understand the common types in use today. Roller bearings are essential in various industries, providing support and reducing friction in moving parts. The most prevalent types include cylindrical, tapered, and spherical roller bearings. Each type has unique features. For instance, cylindrical bearings are ideal for high-load applications due to their increased surface contact.
Cylindrical roller bearings can handle radial loads effectively. A report by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA) notes that these bearings can operate under high speeds, which is significant in manufacturing applications. Tapered roller bearings, on the other hand, support both radial and axial loads. Their versatility makes them a go-to option in automotive functionality. Spherical roller bearings allow for misalignment, making them crucial in heavy-duty machinery.
Despite their advantages, roller bearings are not without flaws. Poor lubrication can lead to premature wear, creating significant downtime. In a study by the International Journal of Industrial Engineering, improper maintenance resulted in a 30% increase in failure rates. This serves as a stark reminder that while roller bearings enhance performance, they require ongoing attention to ensure durability and efficiency.
Key Performance Metrics: Load Ratings and Speed Capacities
Choosing the right roller bearings can significantly impact performance. Load ratings and speed capacities are key factors to consider. Load ratings indicate the amount of weight a bearing can support without failing. They are crucial for machinery operating under heavy loads. Higher load ratings suggest enhanced durability, but they can also lead to increased friction and heat.
Speed capacities refer to how fast a bearing can operate without degrading. Different designs cater to specific speed requirements. Some bearings excel at high speeds but may sacrifice load capacity. It's essential to strike a balance between these metrics. If a system runs too fast for the bearing type, it may lead to premature failure.
It's also important to evaluate material choices. Some materials perform better under specific conditions. For instance, steel offers strength and durability but may not be ideal in corrosive environments. Reflecting on your specific needs is vital. Overlooking either load ratings or speed can hinder overall performance.
2026 Best Roller Bearing Types for Enhanced Performance and Durability
| Bearing Type | Load Rating (kN) | Speed Capacity (RPM) | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Groove Ball Bearing | 20-120 | 6000-8000 | Steel | Electric motors, Pumps |
| Angular Contact Ball Bearing | 25-90 | 4000-6000 | Ceramic, Steel | Machine tool spindles |
| Tapered Roller Bearing | 30-150 | 3000-5000 | Steel | Automotive, Industrial machinery |
| Spherical Roller Bearing | 40-200 | 2000-3000 | Bronze, Steel | Mining, Construction |
| Needle Bearing | 10-50 | 10000-20000 | Steel | Automotive, Aerospace |
Material Composition: Impact on Durability and Friction Reduction
The choice of material in roller bearings significantly affects their performance. Different materials exhibit varying degrees of durability and friction reduction. For instance, steel bearings are popular for their strength and resilience. However, they often generate more heat due to friction. On the other hand, ceramics can be a game-changer. They offer lighter weights and lower friction coefficients, which enhance overall performance. According to industry reports, ceramic bearings can reduce friction by up to 50% compared to traditional steel counterparts.
Using composite materials is another strategy to improve performance. These materials can provide a good balance between weight, strength, and thermal stability. Recent studies indicate that hybrid bearings, which combine steel and ceramic, demonstrate improved lifespan and lower operating temperatures. Yet, manufacturing composite materials can be more complex and costly, creating challenges for some applications.
Durability is not solely linked to material choice. Design also plays a critical role. Smaller bearings can perform well under lower loads, but they may wear out faster under heavy use. Understanding the operational environment is essential. Load, speed, and even temperature can greatly influence bearing longevity. Selecting the right materials and designs is crucial, yet often overlooked in the pursuit of enhanced performance.
Applications and Industries: Where Roller Bearings Make a Difference
Roller bearings are versatile components widely used in various industries. Their ability to reduce friction enhances efficiency in machines. In automotive applications, roller bearings support wheels, axles, and driveshafts. This support allows for smooth operation and safety.
Similarly, in manufacturing, roller bearings are essential in conveyor systems, ensuring seamless movement of goods.
Tips: Regular maintenance is crucial. Inspect bearings for wear and replace them as needed. This practice can prevent unexpected failures.
In the aerospace sector, roller bearings must withstand extreme conditions. They play a vital role in aircraft engines, ensuring reliability. Additionally, in robotics, these bearings enable accurate movement and positioning. However, choosing the right type of bearing can be challenging. Not every bearing fits every application. Taking the time to evaluate specific needs is essential.
Tips: Always consider load capacity and speed requirements. This approach helps in making informed decisions. When in doubt, ask for expert advice.
Future Trends: Innovations in Roller Bearing Technology for 2026
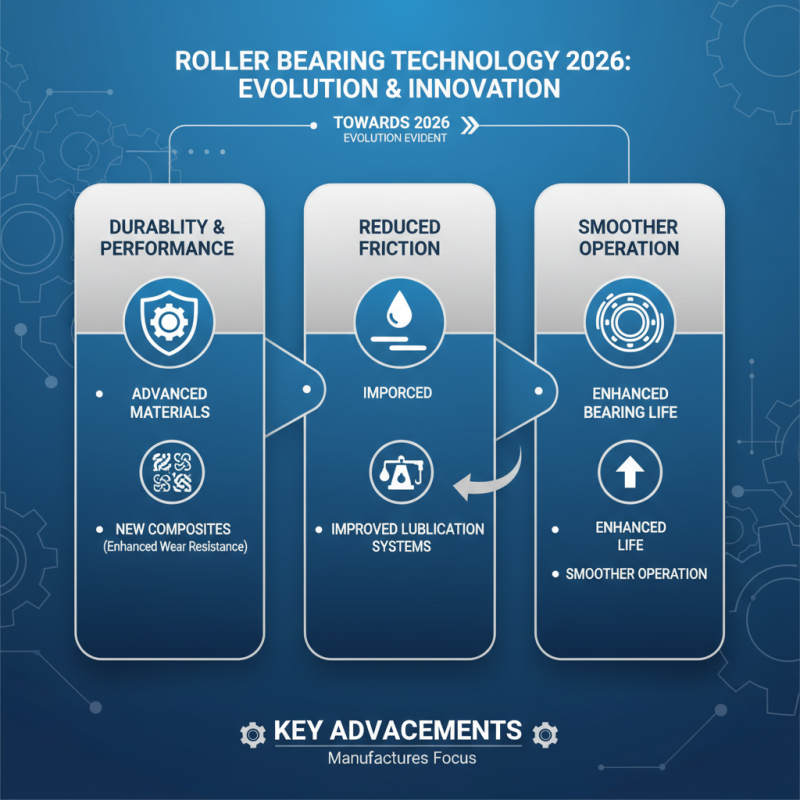
As we approach 2026, the evolution of roller bearing technology is evident. Manufacturers are focusing on materials that enhance durability and performance. Innovations include improved lubrication systems. These advancements reduce friction, allowing for smoother operation. New composites are being tested, promising better wear resistance.
Sustainability is also a priority. Some producers are exploring biodegradable materials. These materials might diminish environmental impact but can compromise structural integrity. The challenge lies in balancing sustainability with performance. It’s essential to consider how these shifts in material might affect longevity.
Moreover, smart technology integration is expanding. Sensors embedded in bearings provide real-time data. Businesses can monitor performance closely. However, reliance on technology raises concerns. What if the technology fails? Maintenance practices must evolve alongside these innovations. The future of roller bearings could greatly enhance efficiency, yet it demands careful reflection on the potential trade-offs.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Small Bearing for Your Project?
-
Top 2025 Guide to Flange Bearings Applications and Benefits Explained
-

Exploring the Science Behind Miniature Bearings and Their Role in Modern Technology
-

How to Choose the Right Hardware Bearing for Your Project?
-

2025 Top 10 Linqing Bearings: Discover the Leading Brands and Innovations
-

2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Miniature Ball Bearings for Your Project
-

Phone
-

E-mail
-

Whatsapp
-

Wechat
Wechat





